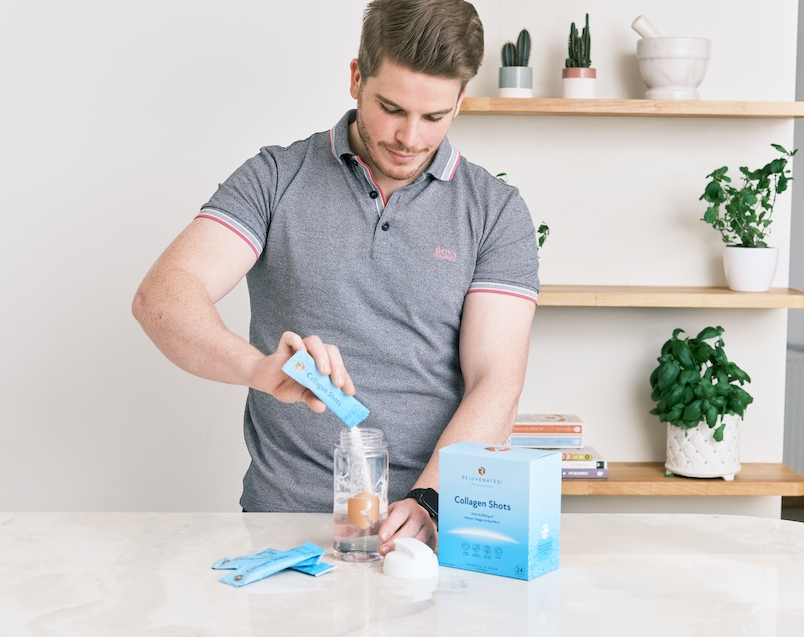
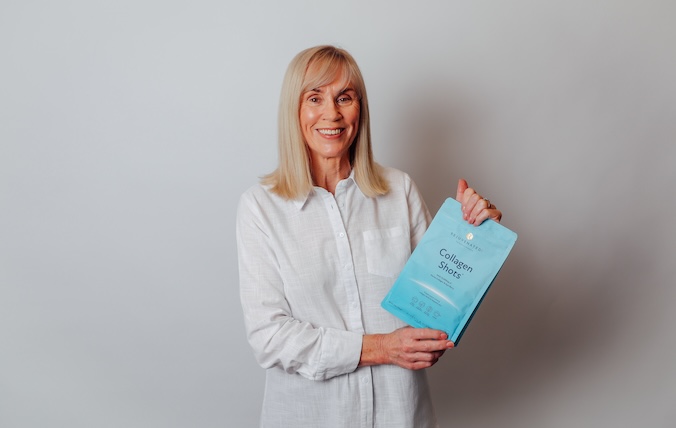
Q: Do you have scientific references?
A: Yes - please see our references here -… Read more
Barnett, M.L., Kremer, J.M., St. Clair, E.W., Clegg, D.O., Furst, D., Weisman, M., Fletcher, M.J., Chasan-Taber, S., Finger, E., Morales, A., Le, C.H. & Trentham, D.E. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with oral type II collagen: results of a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1998; 41:290–297.
Baumann, L. Skin ageing and its treatment. J Pathol. 2007 Jan; 211(2):241-51.
Bos, J.D. & Meinardi, M.M. The 500 dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp Dermatol. 2000; 9:165–169
Bruyère, O., Zegels, B., Leonori, L., Rabenda, V., Janssen, A., Bourges, C. & Reginster, J.Y. Effect of collagen hydrolysate in articular pain: a 6-month randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study. Complement Ther Med. 2012; 20(3):124-30.
Carpenter, R.L., Peel, J.B., Carpenter, M.R., Lowndes, J., Angelopoulos, T.J. & Rippe, J.M. Effectiveness of a collagen hydrolysate-based supplement on joint pain, range of motion and muscle function in individuals with mild osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64: 1544.
Cho, K-H., Hong, J-H. & Lee, K-T. Monoacylglycerol (MAG)-Oleic Acid has stronger antioxidant, anti-atherosclerotic, and protein glycation inhibitory activities than MAG-palmitic acid. J Med Food. 2010; 13:99–107
Choi, S.Y., Kim, W.G., Ko, E.J., Lee, Y.H., Kim, B.G., Shin, H.J., Choi, Y.S., Ahn, J.Y., Kim, B.J. & Lee, H.J. Effect of high advanced-collagen tripeptide on wound healing and skin recovery after fractional photothermolysis treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014; 39(8):874-80.
Chung, J.H., Seo, J.Y., Choi, H.R., Lee, M.K., Youn, C.S. & Rhie, G. Modulation of skin collagen metabolism in aged and photoaged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2001; 117:1218–1224
Cosgrove, M.C., Franco, O.H., Granger, S.P., Murray, P.G. & Mayes, A.E. Dietary nutrient intakes and skin-aging appearance among middle-aged American women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 86:1225-1231.
Di Lullo, G.A., Sweeney, S.M., Körkkö, J., Ala-Kokko, L. & San Antonio, J.D. Mapping the Ligand-binding Sites and Disease-associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I Collagen. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(6):4223-4231.
Fligiel, S., Varani, J., Datta, S., Kang, S., Fisher, G. & Voorhees, J. Collagen degradation in aged/photodamaged skin in vivo and after exposure to matrix metalloproteinase-1 in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:842–848.
Gilchrest, B.A. Skin aging and photoaging: an overview. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989; 21:610–3.
Grattagliano, I., Palmieri, V.O., Portincasa, P., Moschetta, A. & Palasciano, G. Oxidative stress-induced risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome: a unifying hypothesis. J Nutr Biochem. 2008; 19:491-504.
Grinnell, F. Fibroblast biology in three-dimensional collagen matrices. Trends Cell Biol. 2003; 13(5):264-9.
Iwai, K., Hasegawa, T., Taguchi, Y., Morimatsu, F., Sato, K., Nakamura, Y., Higashi, A., Kido, Y., Nakabo, Y. & Ohtsuki K. Identification of food derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem. 2005; 53:6531–6536.
Kadison, E.D. Effect of gelatin on the vascularity of the finger. Angiology. 1965; 170-176
Kajimoto, O., Odanaka, W., Sakamoto, W., Yoshida, K., Takahashi. Clinical effects of Hyaluronic Acid Diet for Dry Skin. J New Reme & Clinics. 2001; 50(5): 548-560.
Kantor, I., Donikyan, L., Simon, R., & Wollschlaeger, B. Results of a study evaluating the use of a dietary supplement formula in the management of age-related skin changes in women with moderate to severe wrinkling of the periorbital area. JANA. 2002; 5(2):10-19.
Kennedy, C., Bastiaens, M.T. & Bajdik, C.D. Effect of smoking and sun on the aging skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 120:548–554
Koyama, Y. Effects of collagen peptide ingestion on the skin. Shokuhin-To-Kaihatsu. 2009:44:10-12.
Longas, M.O., Russell, C.S. & He, X.Y. Evidence for structural changes in dermatan sulfate and hyaluronic acid with aging. Carbohydr Res. 1987; 15: 159(1):127-36.
Martin, A. (2001). Advanced nutritional intakes (Ed.) Tec. & Doc, Paris.
Matsuda, N., Koyama, Y., Hosaka, Y., Ueda, H., Watanabe, T., Araya, T., Irie, S. & Takehana, K. Effects of ingestion of collagen peptide on collagen fibrils and glycosaminoglycans in the dermis. J Nut Sci & Vitaminol. 2006; 52:211-215.
Matsumoto, H., Ohara, H., Ito, K., Nakamura, Y. & Takahashi, S. Clinical effect of fish type I collagen hydrolysate on skin properties. ITE Lett Batteries New Technol Med. 2006;7:386-390.
McAlindon, T.E., Nuite, M., Krishnan, N., Ruthazer, R., Price, L.L., Burstein, D., Griffith, J. & Flechsenhar, K, Change in knee osteoarthritis cartilage detected by delayed gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging following treatment with collagen hydrolysate: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis & Cartilage. 2011; 399–405
McCrorie, T.A., Keaveney, E.M., Wallace, J.M.W., Binnsa, N., Livingstone, M. B. E. Human health effects of conjugated linoleic acid from milk and supplements. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2011; 24:206-227.
McEniery, C.M., Wilkinson, I.B. & Avolio, A.P. Age, hypertension and arterial function. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007; 34(7):665-71.
Mertens-Talcott, S.U., Rios, J., Jilma-Stohlawetz, P., Pacheco-Palencia, L.A., Meibohm, B. & Talcott, S.T. Pharmacokinetics of anthocyanins and antioxidant effects after the consumption of anthocyanin-rich acai juice and pulp (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) in human healthy volunteers. J Agric Food Chem. 2008; 56:7796-7802.
Miller, E.J. Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetically distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochen. 1976; 13:165-192.
Moskowitz, R.W. Role of collagen hydrolysate in bone and joint disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 30:87 – 99.
Oesser, S., Adam, M., Babel, W. & Seifert, J. Oral administration of (14)C labeled gelatin hydrolysate leads to an accumulation of radioactivity in cartilage of mice (C57/BL). J Nutrition. 1999; 129:1891-1895.
Ohara, H., Ichikawa, S., Matsumoto, H., Akiyama, M., Fujimoto, N., Kobayashi, T. & Tajima S. Collagen-derived dipeptide, proline-hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol. 2010; 37(4): 330–338.
Ohara, H., Matsumoto, H., Ito, K., Iwai, K. & Sato, K. Comparison of quantity and structures of hydroxyproline- containing peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates from different sources. J Agric Food Chem. 2007; 55:1532–1535.
Peterkofsky, B. Ascorbate requirement for hydroxylation and secretion of procollagen: relationship to inhibition of collagen synthesis in scurvy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991; 54:1135S-1140S.
Phillips, C.L., Combs, S.B. & Pinnell, S.R. Effects of ascorbic acid on proliferation and collagen synthesis in relation to the donor age of human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1994; 103:228-232.
Postlethwaite, A.E., Seyer, J.M., and Kang, A.H. Chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to type I, II, and II collagens and collagen-derived peptides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1978; 75(2): 871-875.
Purba, M.B., Kouris-Blazos, A. & Wattanapenpaiboon, N. Skin wrinkling: can food make a difference? J Am Coll Nutr. 2001; 20:71-80.
Rexbye, H., Pettersen, I., Johansen, M., Kiltkou, L., Jeune, B. & Christensen, K. Influence of environmental factors on facial ageing. Age & Ageing. 2006; 35:110-115.
Rhie, G., Shin, M.H. & Seo, J.Y. Aging- and photoaging-dependent changes of enzymic and nonenzymic antioxidants in the epidermis and dermis of human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2001; 117:1212-1217.
Richelle, M., Sabatier, M., Steiling, H. & Williamson, G. Skin bioavailability of dietary vitamin E, carotenoids, polyphenols, vitamin C, zinc and selenium. Br J Nutr. 2006; 96(2):227–238.
Rosenberg, S., Oster, K.A., Kallos, . & Burroughs, W. Further studies in the use of gelatin in the treatment of brittle nails. Arch Dennat and Syph. 1957; 76:330-5.
Sales-Campos, H., Souza, P.R., Peghini, B.C., da Silva, J.S. & Cardoso, C.R. An overview of the modulatory effects of oleic acid in health and disease. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013; 13(2):201-10.
Sato, T., Sakamoto, W., Odanaka, W., Yoshida, K. & Urushibara, O. Clinical effects of dietary hyaluronic acid on dry, rough skin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2002; 12:109–120
Scala, J., Hollies, N.R.S. & Sucher, K.P. Effect of daily gelatine ingestion on human scalp hair. Nut Rep Int. 1976; 13(6):579–592
Schauss, A.G., Wu, X., Prior, R.L., Ou, B., Patel, D. & Huang, D. Phytochemical and nutrient composition of the freeze-dried amazonian palm berry, Euterpe oleraceae mart. (acai). J Agric Food Chem. 2006; 54:8598-8603.
Schwimmer, M. & Mullnos, M. Salutary effects of gelatin on nail defects in normal subjects. Antibiotic Med & Clin Ther.. 1957; 4:403-7.
Sumida, E., Hirota, A. & Kuwaba, K. The effect of oral ingestion of collagen peptide on skin hydration and biochemical data of blood. J Nutr Food?. 2004;7:45-52.
Uitto, J. Connective tissue biochemistry of the aging dermis. Age-related alterations in collagen and elastin. Dermatol. Clin. 1986; 4:433–446.
Varani, J., Warner, R.L. & Gharaee-Kermani., M. Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 114:480–486.
West, M.D. The cellular and molecular biology of skin aging. Arch Dermatol. 1994; 130(1):87-95.
Collapse





_804x637.jpg)